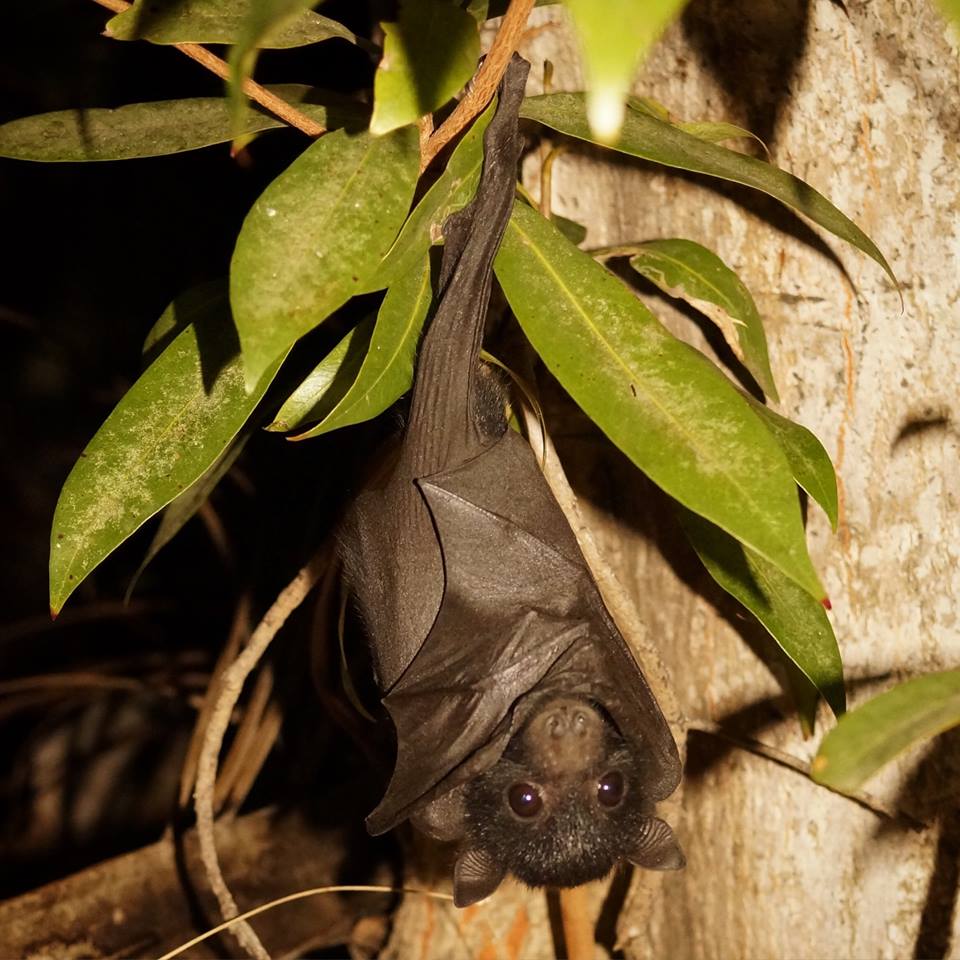
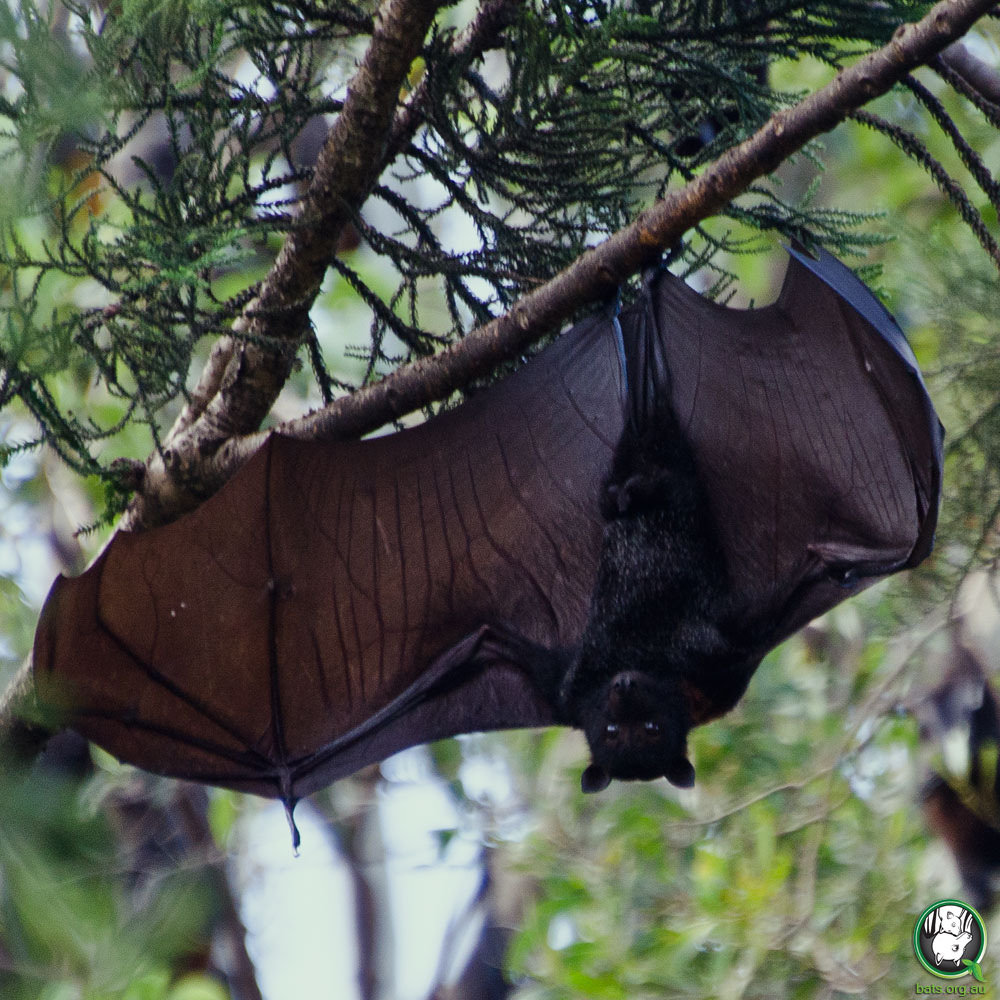
Behaviour
Call
Loud, high-pitched squabbling.
Diet
It prefers pollen and nectar from eucalypt blossoms, paperbarks and turpentine trees; however, it may also eat other native and introduced flowers and fruit, including mangoes, when native foods are scarce. It has also been seen feeding on leaves by chewing them, swallowing the liquid and then spitting out the fibre.
Movement
During the day it roosts on tree branches in large groups known as camps. Main camps form during summer and their size varies depending on the availability of local food. It leaves the camp at dusk to feed, finding its food by sight and smell, and by following other bats. The groups can travel over 50 km to feed and will use the same camp for many years.
Breeding
Mating occurs in autumn and the female gives birth in late winter or spring when food is abundant. The young are carried by their mothers until they are about four weeks old when they are left at the roost while their mothers forage at night. They begin to fly when they are eight weeks old but remain dependent on their mothers for at least three months.
Field Guide
Improve your identification skills. Download your Black Flying Fox field guide here!