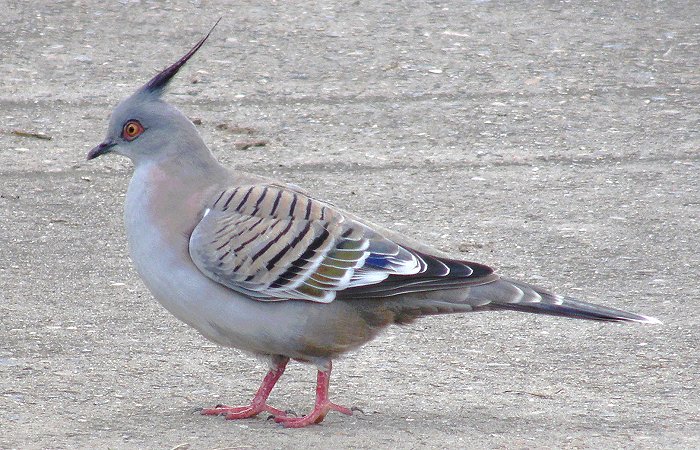
Size
36 – 44 cm long (from head to tail), with an average wing span of 76 cm
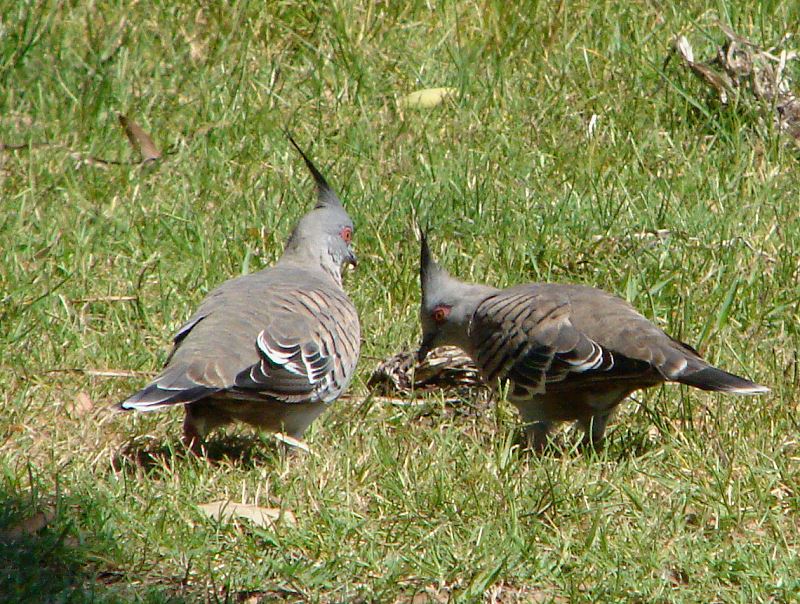
Behaviour
Call
A carolling, flute-like song, often calling together.
Diet
The Crested Pigeon feeds on native seeds, as well as those of introduced crops such as wheat and weeds. Some leaves and insects are also eaten.
Flight
Swift, strong and direct, sometimes in flocks of several hundred birds.
Breeding
It is extremely territorial during the four to six weeks of the breeding season. The female usually selects a nest site, which is either high up a tree, on a power pole or on the roof of a building. The nest is a rough basket of sticks, twigs, plant stems and occasionally wire, lined with softer materials such as wool, hair, grass, feathers and shredded bark. The female lays between one and six eggs, which are either blue or green with brown blotching, and she sits on them for 20 days. She then feeds her young until they are about four weeks old, when they are ready to fly and leave the nest.
Field Guide
Improve your identification skills. Download your Crested Pigeon field guide here!