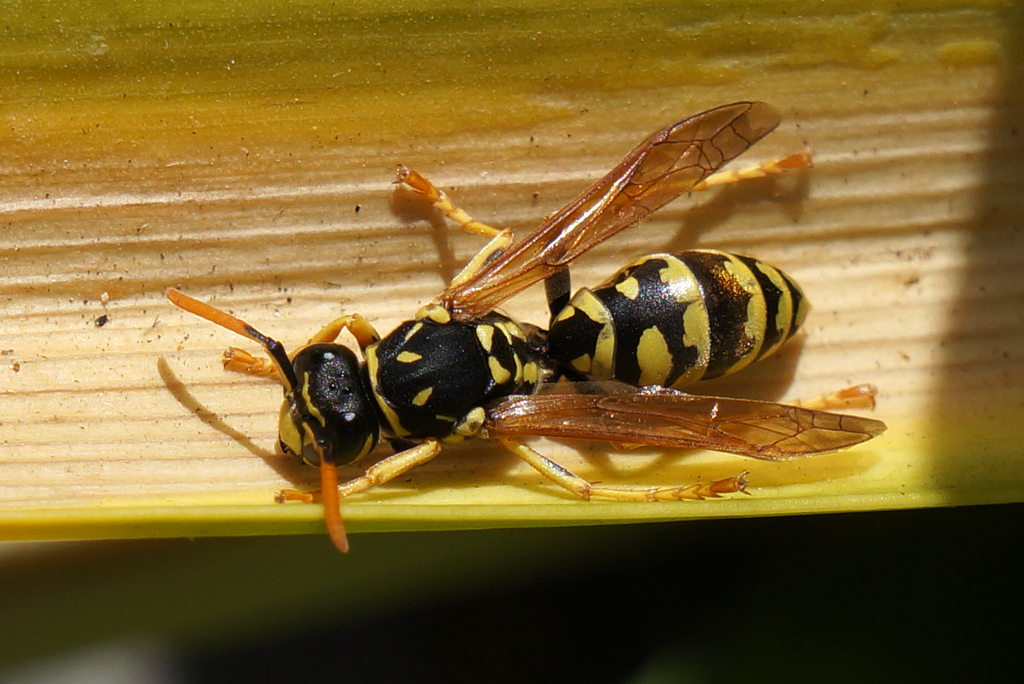
Behaviour
Diet
Meat products, including fish, and sweet foods. It travels up to 500 metres from its nest to search for food. Grubs in the nest are fed insects, spiders and pieces of meat.
Flight
Very fast, holding its legs close to its body. It doesn’t usually hover.
Breeding
Mating occurs in autumn, after which the males die. The mated females (queens) disperse to hibernate over the winter, although one queen may remain in the original nest. In spring, the queens emerge and search for a nest site. They construct a nest from papery material scraped from wood and mixed with saliva. The queen makes about a dozen cells inside the nest, and lays an egg in each cell. The eggs hatch into larvae, which are fed by the queen until they pupate and become worker wasps in late spring or early summer. The workers enlarge the nest (often to the size of a football) and gather food, while the queen continues to lay eggs. The number of wasps in the nest peaks in early autumn, often with up to 2,000 workers! Male wasps (drones) are produced, followed by new queens in late autumn when the original queen dies. The new queens and drones then mate outside the nest.
Field Guide
Improve your identification skills. Download your European Wasp field guide here!